Entity-oriented Search Understanding is an important part of Search Engine Understanding or Search Engine Communication. These terms might be new to the traditional understanding of SEO, but the process of understanding a search engine is a daily routine for any SEO to analyze the search engines’ decision trees that create their result pages. Entity-oriented Search Understanding is the understanding of a SERP Instance based on entities, their types, attributes, and connections to each other. A search engine might choose only certain types of pages that include a type of entity along with particular attributes and phrase variations for these attributes with the most related facts. Or, a search engine might filter the results according to the sources’ N-Grams for certain entities. If they don’t have enough numbers, or if they don’t have the relevant facts and external references for these entities, it might be outranked.
With entity-oriented search understanding, an SEO can have a better and deeper vision for the search engines. Knowing an entity from a topic, its contextual layers, and relation types with other entities are crucial to help a source (website) rank higher on the query results of a web search engine. In this article, entity-oriented search engine optimization, and its effect on a Broad Core Algorithm Update’s results, will be explained with a real-world SEO Case Study which is BKMKitap.com.

Before continuing, you can find the related information for the author of this SEO Case Study and examination.
“By implementing entity-focused SEO perspective with innovation, and following the new SEO Concepts, we were able to regain the lost organic traffic due to the latest Google Broad Core Algorithm Updates. By focusing on Core Algorithm Updates to improve the authority of BKMKitap.com with Koray’s guidance, we have created more granular and detailed content for e-commerce and informative web pages.”
Haluk Bolaban,
BKMKitap.com Marketing Director
Background of the Entity-oriented Search Understanding Case Study BKMkitap
The last 5 broad core algorithm updates of Google were mostly negative until July 3, 2021, Broad Core Algorithm Update.
- July 3, 2021, Broad Core Algorithm Update (Strongly Positive)
- June 2, 2021, Broad Core Algorithm Update (Neutral)
- December 3, 2020, Broad Core Algorithm Update (Harshly Negative)
- May 4, 2020, Broad Core Algorithm Update (Neutral)
- January 13, 2020, Broad Core Algorithm Update (Negative)
- June 2, 2019, Broad Core Algorithm Update (Negative)
BKMkitap.com is one of the biggest book stores in Turkey, and it is one of the rare situations where a website has a strong search demand, and lots of navigational queries but still loses all of the broad core algorithm updates despite there being no untrustworthiness or non-expertise signals on the open web.
However, BKMKitap.com has a tremendous amount of Technical SEO and Web Page Loading Performance Optimization problems. Below, you can see a general overview of the Google Search Mobile Pagespeed report for the BKMKitap.com.
I try to keep only the “valid” section high in the Google Search Console Coverage Report. This is so search engines can focus on only indexing and ranking rather than understanding which URL is necessary on the SERP with which version; this includes how to parse, digest HTML, or understand the content, etc. Below, you can see the heavy canonicalization errors along with the other mixed indexing signals.
Below, you can see the good URLs of BKMKitap.com in the Page Experience Report of the GSC, if you are lucky enough to see them one day.
To demonstrate the Technical SEO and pagespeed related problems of the BKMKitap.com SEO Case Project, you can check the list below.
- Half of the website URLs don’t exist in the sitemaps
- There are millions of cannibalized URLs.
- There are thousands of duplicate product URLs.
- More than 30000 internal 404 pages. (From full data)
- Blocked URLs within the Sitemap.
- Hundreds of 5XX errors daily
- Submitted URLs with Noindex
- Redirection Errors
- Submitted but 404 URLs
- Indexed but blocked URLs (Tens of thousands)
- Indexed contents without actual content
- More than half a million robots.txt excluded pages.
- Nearly 100.000 URLs are crawled and not indexed.
- Nearly 53.224 pages are currently discovered and not crawled.
- Over 600.000 duplicate with canonical and submitted URL is not selected as canonical.
- The site has millions of URLs, but even a single URL doesn’t pass the Core Web Vitals.
- Most of the website has poor scores on the PSI.
- Thousands of AMP Related issues such as referenced AMP URL is not an AMP, or custom javascript, etc.
- Thousands of structured data errors, and missing information for the related products.
- Hundreds of thousands of products without stock information, or stock existence. These last two subjects also affect the search engine’s confidence to rank the specified e-commerce page, since the stock information, brand, reviews, and prices are not clear enough for the evaluation algorithms.
During the BKMKitap.com SEO Case Study, I also optimized lots of technical SEO and pagespeed-related tasks. However, most of the problems are caused by BKMKitap’s external developer company TSoft as they don’t have enough expertise, experience, or understanding of the SEO to finish these tasks. When the company grows, the problems and technical necessities, and task handling obstacles grow too. That’s why having a Holistic SEO perspective is important. Since the technical SEO wasn’t an option to change the status, I had to use the Entity-oriented Search approach.
What is Topical Authority for Entity Oriented Search?
Topical Authority is the relevance of a source to a topic by proposing link value to the Search Engines by satisfying the users via the queries that seek answers for certain entities with a certain context. Topical Authority is a fundamental term for Semantic SEO to describe the value of the Natural Language Understanding of the search engines.
How to Improve Topical Authority with Entity-oriented Search Understanding?
To improve the topical Authority, a source should cover all the related details to a topic with a certain context, query, and intent template by satisfying the related and possible search intents. To improve the topical authority, the “keyword gap” is not as important as the “information gap”. The facts which exist within a source for a topic, their accuracy, and clarity, position are important to increase the contextual signals of a web page.
To improve the topical authority of an SEO Project, in the context of entity-oriented search, the methods below can be used.
- Compare the entities within different web pages.
- Compare the context and content angle for these entities.
- Compare the facts, prepositions, and semantic role labels for these entities.
- Compare the questions on the competing web pages.
- Compare the Site-wide and Page-level N-Grams of the web pages.
- Compare the web page layout of the web pages (web page design can affect the meaning and context of the entities within the web page)
- Compare the anchor texts from outgoing, and incoming links for these web pages.
- Take all of the attributes of the specific entity, and give them an order based on the relatedness of the attribute for the source, and the popularity of the attribute to generate better questions.
- Use a clear sentence structure for all of the prepositions.
- Do not dilute the context of the web page with irrelevant opinions, or analogies, and other types of entities.
- Process the same entity or same entities from the same type with the same context from start to end.
If you want to learn more about the contextual search, you can read an SEO Case Study that uses question and answer generation for certain topics. Besides these methods, there are many more things that can be used to improve topical authority, contextual relevance, click satisfaction possibility. I will be creating a course to teach Semantic SEO and Semantic Search Engine’s nature to detail all possible steps together.
How to Use Topical Authority for E-commerce Sites with Entity-oriented Search Understanding?
To use the topical authority for e-commerce sites, a source should cover product, brand, services, and dimensions, attributes of these with related information. This information includes price, color, size, availability, shipping, or refund policy, usage guideline, and product-related questions, reviews, or comparisons. Definitional, informational, comparison-based, opinion-based, review-based, factual, and commercial content should exist at the same time within an e-commerce site to make a source topically authoritative for certain types of entities with different contextual layers.
Informational content and commercial content support each other to satisfy every possible, and relevant search activity from the same source. A source should process the related attributes by answering the questions that can be generated from these attributes. If an e-commerce site is about “electronic bikes”, the source should cover “mountain electronic bikes”, “fat-tire electronic bikes”, their parts, invention, maintenance along with similar “bike types”, or its “alternatives”, and “electronic bike brands, products, facts, tips, usage, obstacles, advantages” and more. All these knowledge domains will include different questions with different word distribution possibilities. Moreover, the possible search intents, correlated queries, sequential queries, entity-seeking queries, and query themes should be used to cover these knowledge domains with the best possible contextual vector.
If you don’t know what a “query theme” and “query template” are, you should read the “Indexing SEO Case Study” that I have written to conceptualize the cost of document for indexing along with the cost of not indexing the document. With simple steps, the usage methods of topical authority for e-commerce sites are described in the list below.
- Understand the dimensions of the product that you sell.
- Find all of the relevant entities for the product, including its brand, material, inventor, alternatives, and similars.
- Generate the best proper questions for these dimensions of the product, brands, related entities, and their attributes.
- Give the questions a proper order based on the web page layout, and web page purpose.
- Match the query and answer format with NLP convenient sentence structures.
- Use information redundancy, and unique value opportunities for the products.
- Connect all the entities based on their ontology for commercial purposes.
- Understand the popularity of entity attributes and relatedness of entity attributes.
- Try to use entity relations, relation types, semantic role labeling, and entity resolution from the eyes of the search engines.
- Use phrase templates, phrase pattern taxonomies, and create a prominence hierarchy without diluting the context.
- Search Engines’ perspectives for a topic and the central context of the topical map should align with each other to make search engines understand the website easier, and faster.
How to Understand Which Entity Attributes are More Important for a Context?
The prominence of the attribute, relatedness of an attribute, and popularity of an attribute have different importance levels. An entity attribute can be popular, but it might not be prominent. It can be related to the specific contextual domain, but it might not be prominent enough. And, entity attribute popularity can be seen in two different ways, one is the relatedness of the attribute with different synonyms and query patterns, the other one is the total search demand for the specific attribute. To improve the contextual relevance of a document to a certain query template, a source might need to process lots of different entities from the same type with the same attributes, questions, and answer formats.
To understand the attribute’s importance for an entity, the entity-oriented search analyst should focus on the source’s context, purpose, and the common attributes of the entities from the same type. For instance, if the source is about Formula One, the important attribute of the car will be the “driver, constructor, engine, top speed, weight”, if the source is about history, the main attribute will be the “inception of cars”, or “inventors”. According to the source, the most common attributes from the same entity type will be most important.
To find the attributes that matter for an entity in order to generate questions, a search analyst can focus on the relatedness of the attribute, and prominence of the attribute. For instance, if the source’s knowledge domain is Formula One, the car’s driver, and race circuits will be more prominent than the lap count, or circuit’s viewer capacity. Some attributes have better popularity, and these search-demand waves or trend changes can protect the ranking of the document during newsworthy events. This can improve the news-focused documents from the same source.
How to Connect Entities to Each Other to Strengthen the Contextual Signals and Relevance?
Creating entity connections based on context is possible by using the perspective of ontology. Every entity will have a mutual part with another entity to create a triple. These triples (one object, two subjects) can be used to form a knowledge graph. Information Graphs that include facts can signal the factuality of the content by improving the relevance of the content for a specific query or need behind the query. In this context, co-occurrent phrases, and co-occurrent entities can shift the context of the document. To connect the entities to each other based on a context, Semantic Annotations should be understood as a concept from Named Entity Recognition. Semantic Annotations can be used to label a document for a specific context. The labeled document for a context can signal a weighted attribute of an entity that is a subject of another object. And, the same object can be a subject for another entity, in other words, an attribute.
These subject-object or entity-attribute switches will change the semantic annotation of the text span, and these semantic annotation changes can be used as “internal links” with a definitive relevance.

To give a little bit further concrete example to deepen the process of entity connections, you will find 5 different named entities below.
- Germany, type country.
- France, type country.
- England, type country.
- Turkey, type country.
- The United States, type country.
All these 5 entities are from the same type which is country, thus they will have the same main attributes. The attribute hierarchy or semantic dependency tree of the entity can be used to understand the priority of the attribute to define an entity. If a search engine sees these 5 entities on a web page with the attributes “currency, bank, finance”, it will understand that the topic is international finance. From this contextual layer, possible queries, search intents, and related search activities, indexed documents, questions will be retrieved from the storage of the search engine to satisfy the user. If the terms from the page include “education, school, classroom”, it will understand that the topic is the educational situation, and programs in these countries. An extra phrase or related attribute here can shift the context, and if context shifts, the attributes will be shifted too. To create the entity connections, these entities should be used with the mutual attributes for a specific context, so that the page can experience ranking signal consolidation.
Germany can be connected to Turkey based on its currency exchange rate, or its populational mutual features. All these entities have millions of different possible connections and connection variations between each other. At the same time, Turkey can be connected to England for external debts, while the United States can be connected to Germany for the dollar index. All these different connections, connection permutations, and relation types will define the page’s relevance, and factuality to the user’s query, and represented queries.
How to Define Entities by Specifying the Context?
An entity can’t change its definition based on languages, but its attributes’ prominence can. Or, an entity’s prominence can change based on context. The general information about an entity can switch, the sentiment can be contrary, and the definition of the entity might alter its shape. A tree as an unnamed entity can be a plant in the context of city planning, or biology. For these two contexts, a tree is completely different. A tree can be a decor for home-balancing, or it can be a figure from a painter’s interpretation. A tree can be a mythological creature or a material for bridges. From architecture to ship construction, or from biology to paper prices, an entity can switch its definition, based on context.
To improve the entities’ precision, and factual information redundancy of the source, the entities should be defined with their functions, importance, usage, benefits, and effects for the specific knowledge domain. If its difference, unique and similar sides, alternatives, and advantages are absent within the web page, or if they are not being able to select easily, the web page might dilute its context, relevance, and informational value for the search engine’s re-ranking, and initial ranking algorithms.
How I Used Entity-Oriented Search Understanding for BKMKitap.com SEO Case Study?
Since there is no way to fix the technical SEO, web page layout, web page loading performance, and user experience-related issues on BKMKitap.com as a result of TSoft issues, I had to use entity-oriented search and optimization. To use entity-oriented search understanding for BKMKitap.com, I have focused on the source’s context which is “book e-commerce”. To cover the informational, and e-commerce-related contextual domains from the same knowledge domain, I need to find the most related attributes for both angles.
During the SEO Case Study, to connect the e-commerce, and informational, definitional contextual domains based on books, I have used the “ontology” and “taxonomy” of these things. When it comes to books, as a product, it has “size, material, author, ISBN Number, price, page count, an image or visual for cover, editor”, when it comes to booking as a literature value, it has an “effect on the subject that it processes, a topic, unique sides, differences, authors, characters, genre, era, style, school and more.” When an SEO understands these two sides of the entity as a product, and artwork, the next step is search intent understanding.
In the context of search intent understanding which is an entirely different topic, an SEO should know that a web page should have a dominant context. In other words, a web page can’t be an e-commerce web page and an informational web page at the same time at the same level. One of these options dominates the other one for the specific web page, and the anchor texts or the web page layout should align with this option. Thus, in the BKMKitap.com SEO Case Study, I have created two different web page types, one is for the books’ e-commerce side, the other one is for books’ literature value along with their authors. An e-commerce web page can have an informational content piece, but if this content is about “buying the book”, and “using the product” along with “refund and delivery policies and conditions”, it would improve the search intent coverage for the related web page.
How I Improved the Contextual Relevance and Topical Authority with Informational Content for Commercial Intents?
To improve the contextual relevance, and topical authority with informational content for commercial intents, an SEO should cover the informational, definitional, and factual hinterland of the topics for the specified products. In this context, I have created a different web page group for the things (entities below).
- Books Genres
- Books from Different Geographies
- Books for Different Geographies
- Authors from Eras
- Authors from Geographies
- Authors from Cultures
- Authors from Ideologies
- Individual Author Biographies
- Author and Book Connections
- Author’s Similarities, Differences, Thoughts, Childhood, and more.
The other important section is question generation, creating a context sharpening entity-oriented search document, and connecting all the relevant facts to each other.
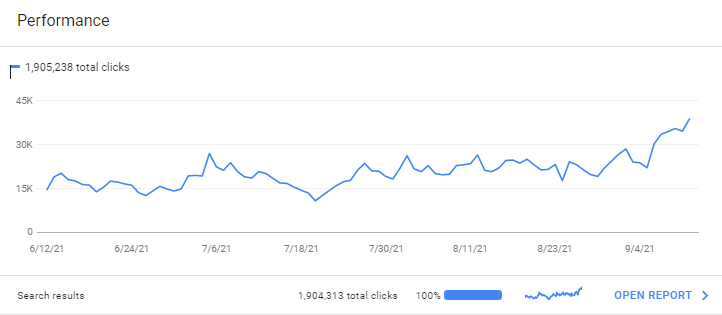
The Effects of the November 2021 Google Broad Core Algorithm Update
The Effects of the November 2021 Google Broad Core Algorithm Update are positive for the BKMKitap.com. The source has earned more than 26.000 new queries on the first day of the November Broad Core Algorithm Update. Most of these queries have both Informational and Commercial characteristics.
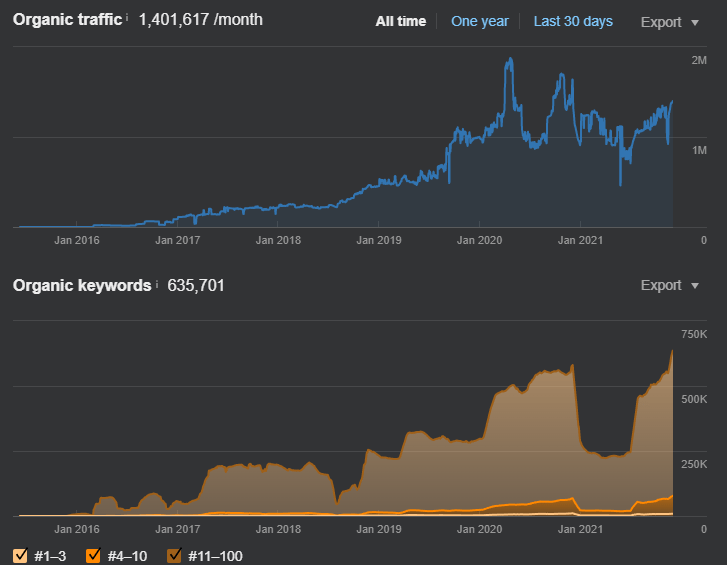
The November 2021 Broad Core Algorithm Update effects for the BKMKitap.com can be seen from SEMRush organic performance metrics and graph as below.
The BKMKitap.com has become the 6th biggest E-commerce Website according to the SimilarWeb Metrics and Data in Turkey.

Semantic SEO has given the BKMKitap.com first-time queries, in other words, the first time, the website ranks for these queries. The same web page with 10 years of experience and historical data can rank the new queries that it didn’t rank before. Semantic SEO and content authorship help a document to have better contextual sharpness and contextual consolidation. Thus, the search engine can rank the specific web page and source of the web pages for a wider contextual domain with a higher confidence score.

BKMKitap.com’s last 7 days change for the Rankings, and Pages with at least one impression. The reason that the active page count increases are that these pages’ contextual coverage and consolidation help them to rank further for the new queries. The historical data that will be acquired from these new queries and new impressions will help for further clicks and better topical authority for new context domains.
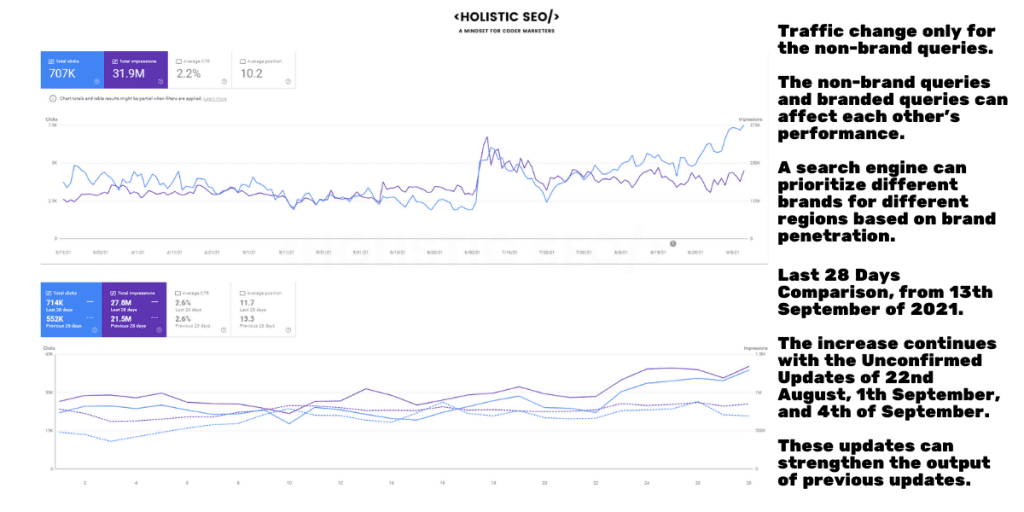
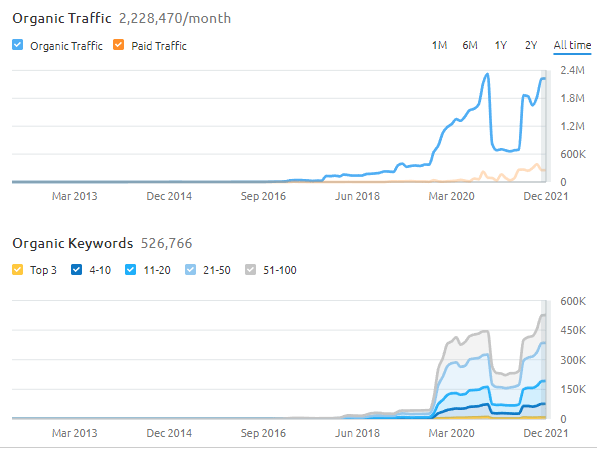
The 2021 Broad Core Algorithm Update, 2021 November Content Spam Update, and 2021 November Local Search Update continued to affect the BKMKitap.com in a positive way. Below, the screenshot can demonstrate the gradual but consistent increase better. The SEMRush Organic Search Performance increase based on Entity-oriented Search Understanding and SEO Strategies can be seen below.
The Organic Performance Report from Ahrefs can be seen below.
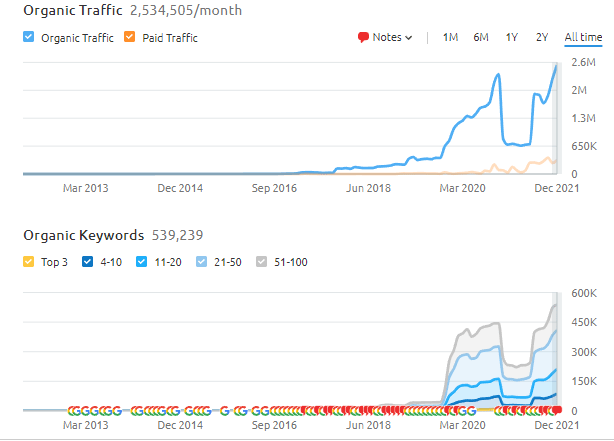
The last 6 months of the performance report of BKMKitap.com can be seen below.
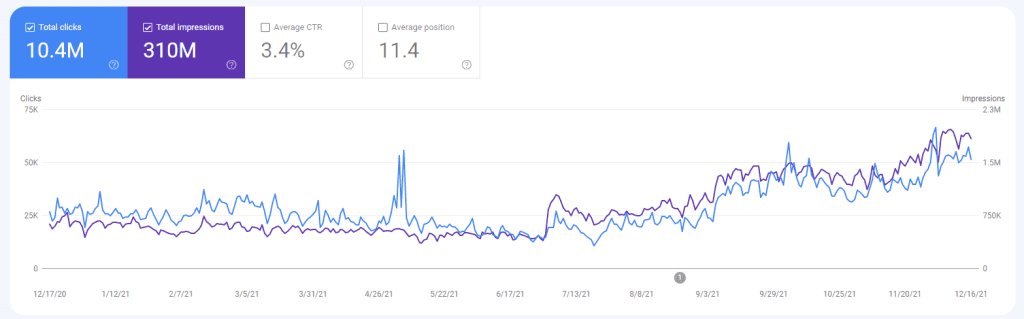
Below, you can see the two weeks later version with an all-time high for BKMKitap.com SEO Case Study and Organic Performance.
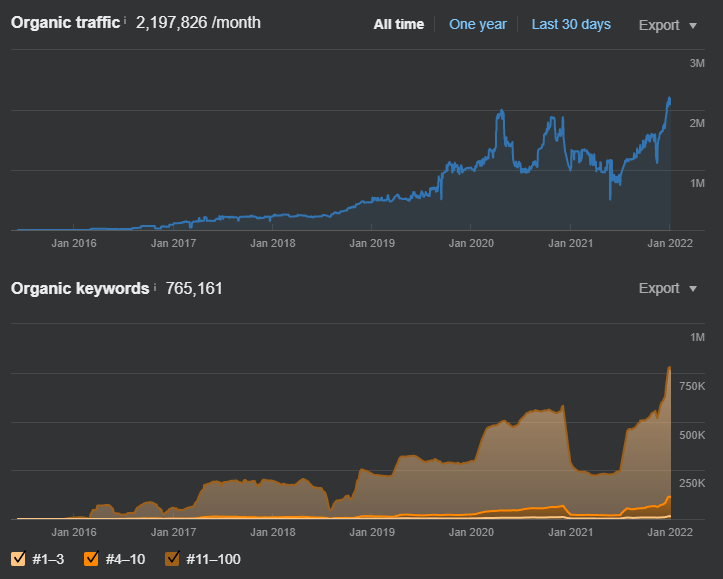
Same Organic Performance change and all-time high values for organic keywords and traffic values can be seen from SEMRush as below.
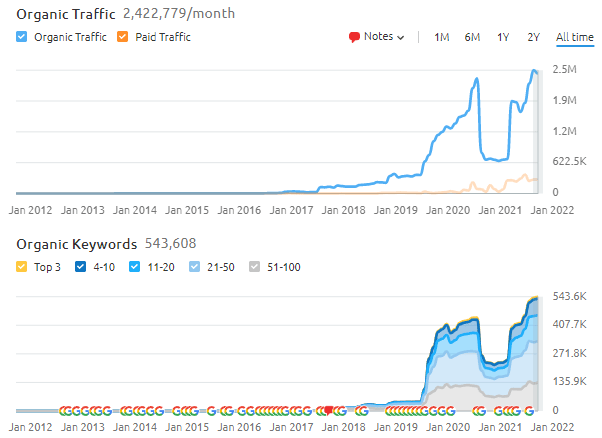
During this timeline, the Semantic Content Network Creation is followed with the same frequency of publication by completing the topical map that covers the related entities, attributes, and contexts. The query count, impressions, and clicks are at the record level for BKMKitap.com via Entity SEO.
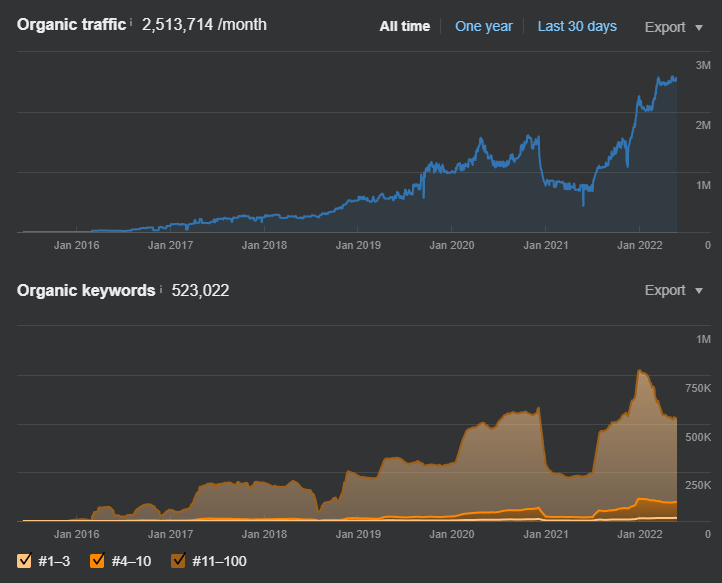
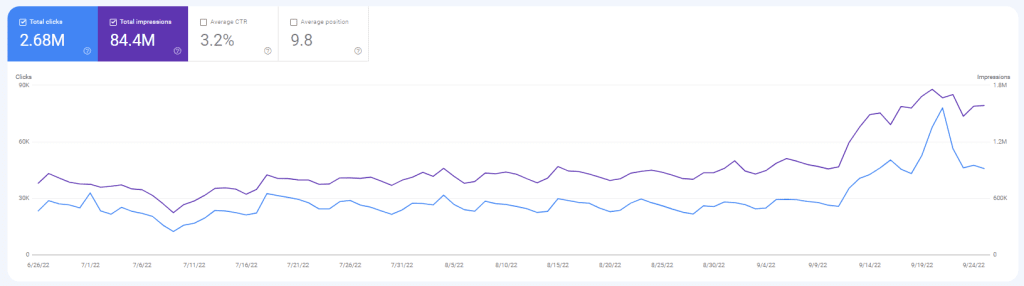
The Effects of the May 2022 and September 2022 Broad Core Algorithm Updates
The effects of the September 2022 Broad Core Algorithm Update for Entity-oriented search SEO Case study are below.
- Over 110% Organic Click Increase,
- 54% Organic Impression Increase,
- %6 Average Position Increase
- Lost 6,000 organic queries
- Gained 1300+ Top 3 Organic Queries
- Gained 5,000+ Top 10 Organic Queries
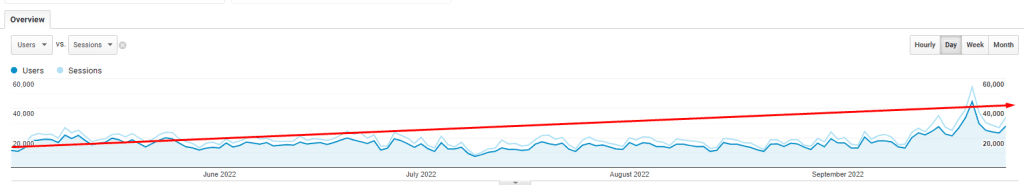
The May 2022 and September 2022 Broad Core Algorithm Updates of Google affected the major news publishers, product reviewers, affiliate marketers, and finance and health industry websites with different percentages. Both of the broad core algorithm updates caused the Google search engine to refresh the SERP Features. Before the Helpful Content Update, and Broad Core Algorithm Update, the Featured Snippet, and People Also Ask SERP features lost their overall existence on the search results. The same timeline created different Featured Snippet tests as below.
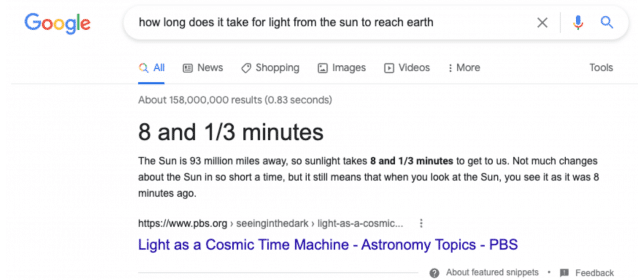
Google published and used “word callouts” based on “consensus” on the featured snippets. And, questions are used as headers to featured snippets as below.

Another featured snippet-oriented test was using the card layout with multiple answers.
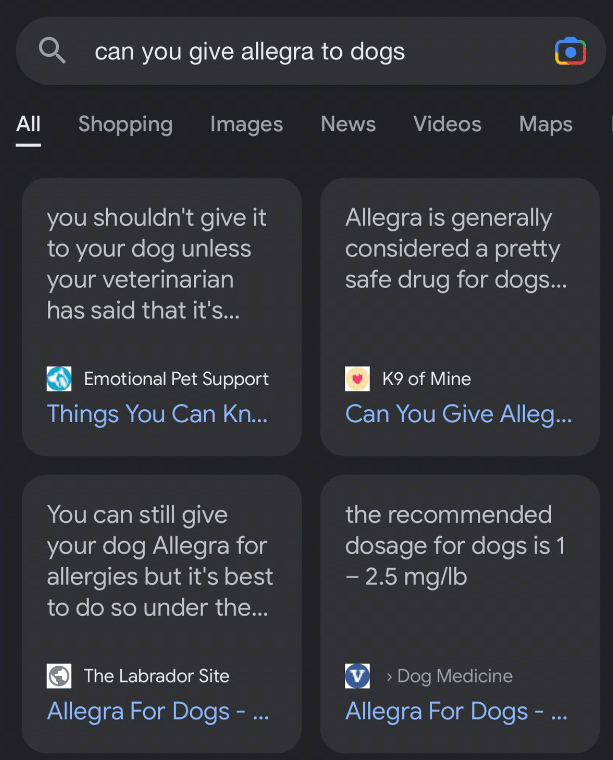
Google tested blue and yellow highlights for the featured snippets.
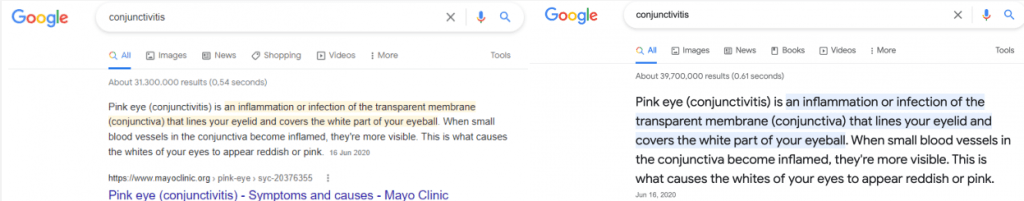
And, another multi-answer featured snippet test is used as below.
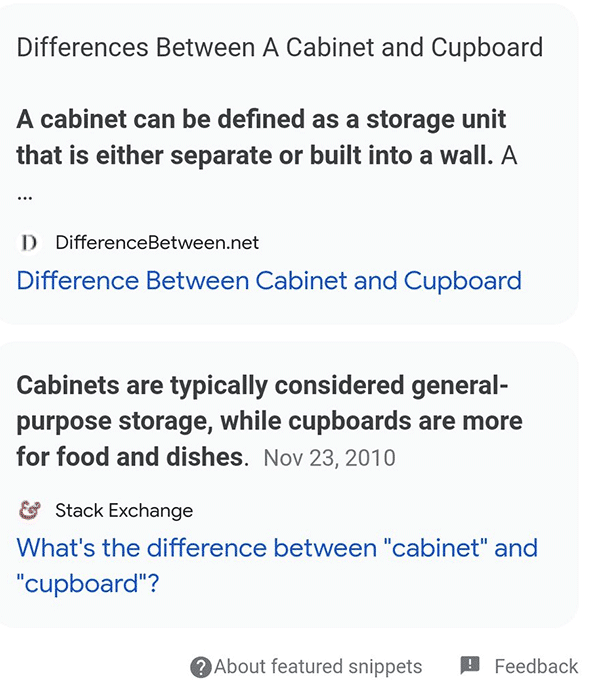
For another “entity-oriented” search feature from Google, such as “People also ask”, we have seen huge drops and raises for the SERP appearances.
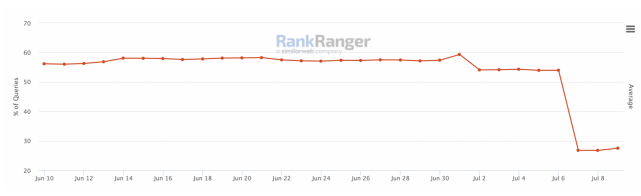
According to RankRanger, on July 6, from 60% to below 30%, the PAA started to lose its coverage for SERP. Then, Google started to show multiple “People also ask” SERP features for the same query.
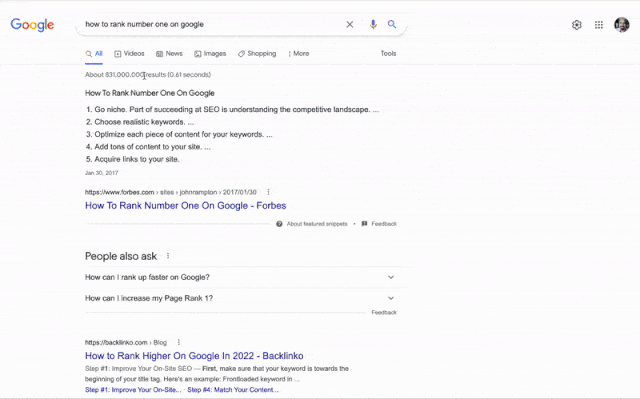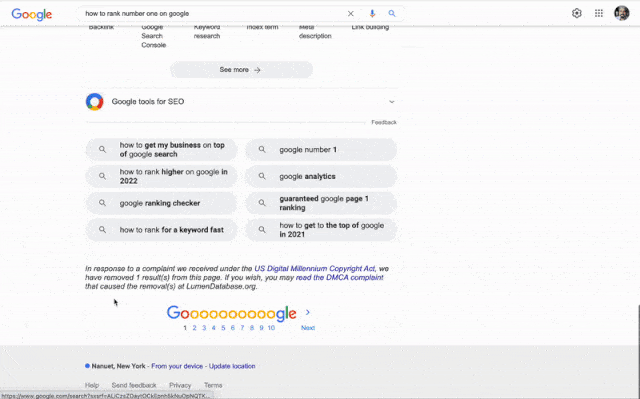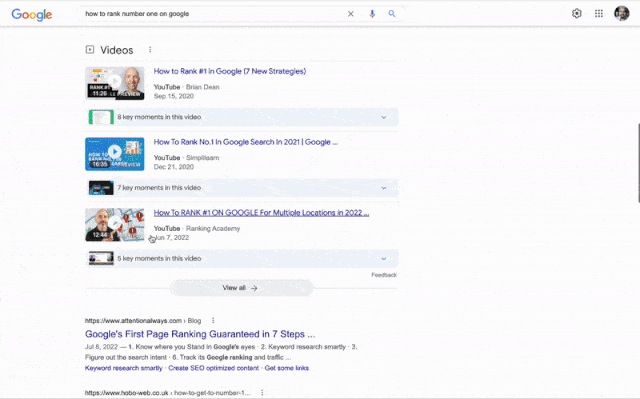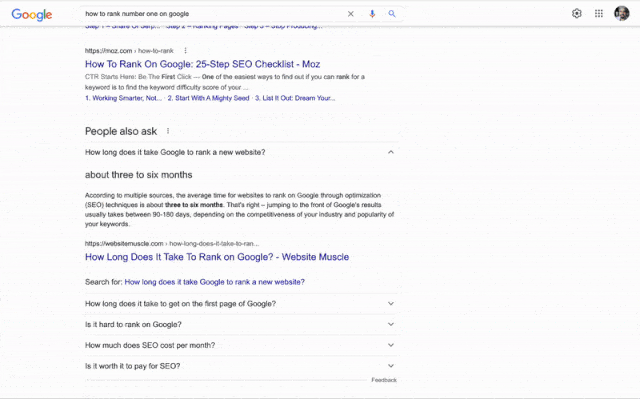
PAA appearance came back to normal levels after 7 days. And, we have seen other types of features such as “Read the full answer” on the PAAs.
We have seen that Google tested “voice PAA” as below.
Google started to show highlights for PAA questions and their answers too.
Google started to decrease the time click gap between the image search, product search, and review aggregation with augmented product panels.
Google made a simple announcement about the edit requests on the Knowledge Panels while changing their design, or starting to serve more entities with their knowledge panels on the SERP.

During the May and September 2022 Broad Core Algorithms Update of Google, the Fifth Product Review Update and Helpful Content Update are launched. The shown tests from Google show that Google focuses on more entity-oriented search. Featured Snippets and People Also Ask questions, answers, and designs are directly related to Information Extraction and Entity-Attribute pairs with query associations.
- The design tests of Google for the specific timeline focus more on “Easy-answers” by differentiating the helpful and responsive content from the less relevant section with highlights, or text bolding.
- The diversification of the “People Also Ask questions” positions show that Google increases the question-answer pairs’ SERP estate.
- Google puts the more relevant and important, closer questions and answers in PAA to the top, while questions from the bottom usually involve the related search terms more.
- Google diversifies the SERP with new results and new answers, and contextual bridges.
- Google leverages different content formats such as audio, or voice answers that appeared during the tests.
- Google uses the card and grid layout, by comparing it to the column layout for serving the multiple answers.
- Google unites multiple verticals of the search under the web (universal) search by adding more connections from visuals, reviews, and brands to regular query results.
- Google resets the Featured Snippets, and PAA SERP features’ appearance with different frequencies with different tests to test different user behaviors for permanent updates.
- The entity-oriented search-related Google updates continued on Google Knowledge Panels by fastening the “edit” requests, changing the entity panels’ subtitles, and changing the designs of the knowledge panels.
There are some other extractions for the Helpful Content Update and Product Review Updates along with their connections to the Broad Core Algorithm Updates.
- Product Review Updates are affecting the E-commerce websites along with the Affiliate Marketers.
- The reviews on the Product page whether it comes from the brand itself, or the users and shoppers, are counted in the product reviews, and feedback.
- Google started to show product reviews from e-commerce websites on the SERP directly with the help of their own Product Graph.
- Websites that increased their traffic from the Helpful Content Update increased their traffic during the September 2022 Broad Core Algorithm Update too.
- Websites that lost traffic during the May 2022 Broad Core Algorithm Update frequently regained their lost traffic with better results during the September 2022 Broad Core Algorithm Update.
- The reversing effect between both of the Broad Core Algorithm Updates might signal a talk from Fabrice Canel on 23 October 2020 from an event of Ryte. Fabrice said that “We do not know which signal weighs more, it is machine learning”. Since, Google uses ML more than “rule-based systems”, these outlier effects, or test, and fix culture might cause more reversing traffic curves between core updates.
- Paul Haahr of Google stated that they prefer updates to be published separately, but there is a lot of “evaluation and debugging” between the BCAUs, and it might be a bottleneck for them to publish more broad core algorithm updates.
- Helpful Content Update focused on “topical relevance” by stating that “a source should write for a topic if the website is relevant to the topic, not just for taking the traffic”.
- Helpful Content Update emphasized the prominence of Information Responsiveness for the factoids, and guides.
- Product Review Update emphasized the first-person experience and unique expertise for the products that are reviewed.
- Google published Link and Content related spam updates during this time.
- September 2022 Broad Core Algorithm update of Google made news publishers lose traffic over the affiliate marketing content.
- September 2022 Broad Core Algorithm Update made Government websites gain more traffic for the governmental questions which affected news publishers again.
- Both of the Broad Core Algorithm Updates increased the total number of domains that get traffic from different topics while sharing the SERP item ranks with more diversification.
- Google published and announced new language models such as PALM, or Cost-Effective and Adaptive Language Model, Quantization for Fast and Environmentally Sustainable Reinforcement Learning, and Generalized Object Localization with Natural Language Queries.
- Google launched the Imagen for Image-to-text and Text-to-image generation with AI.
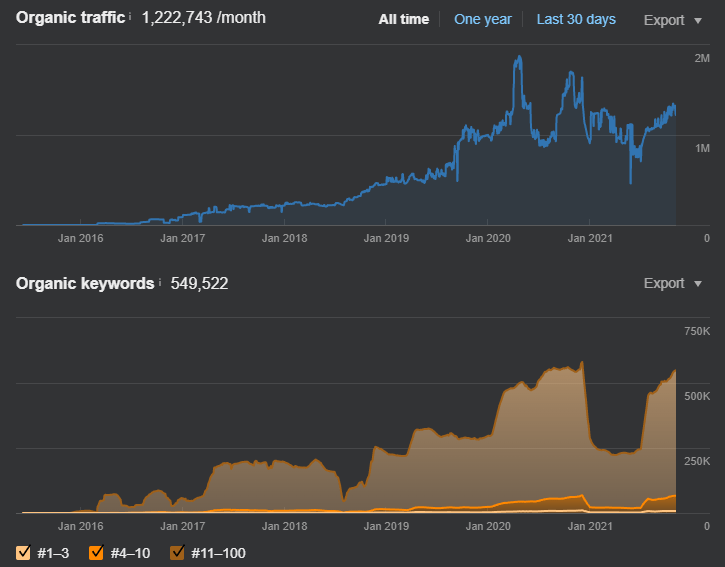
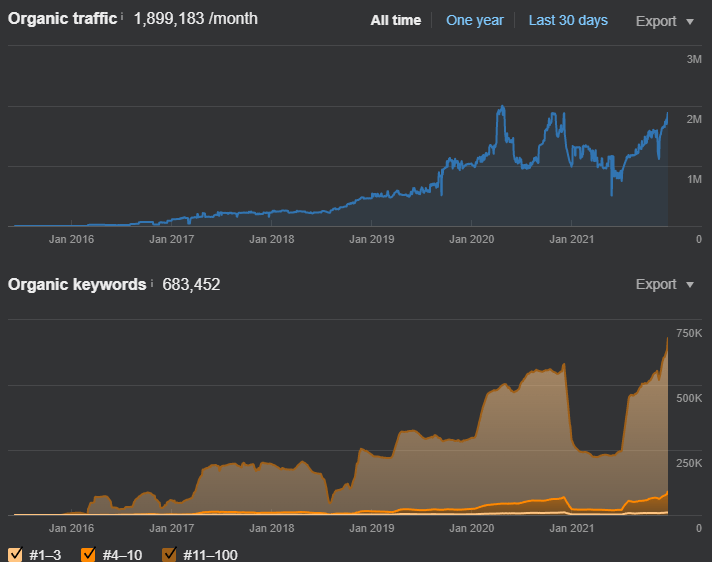
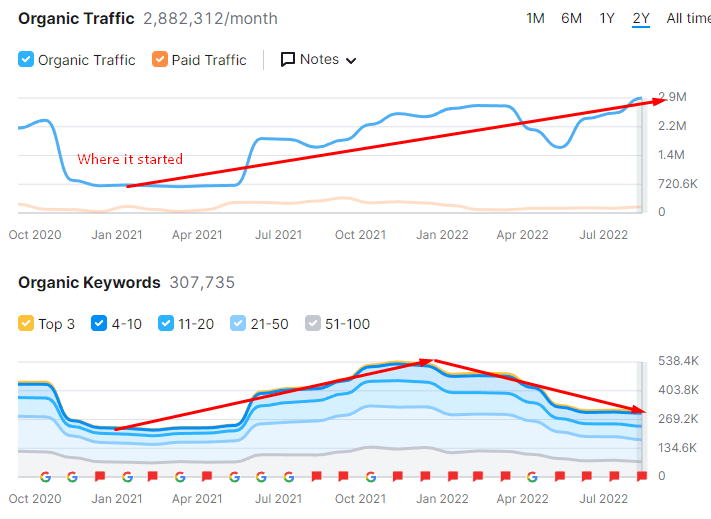
All the updates, tests and publications, or research from Google should be united when an SEO tries to understand entity-oriented search further and further. The BKMKitap.com SEO Project increased its organic traffic by over 112%. The SEMrush organic search performance graphic is below.
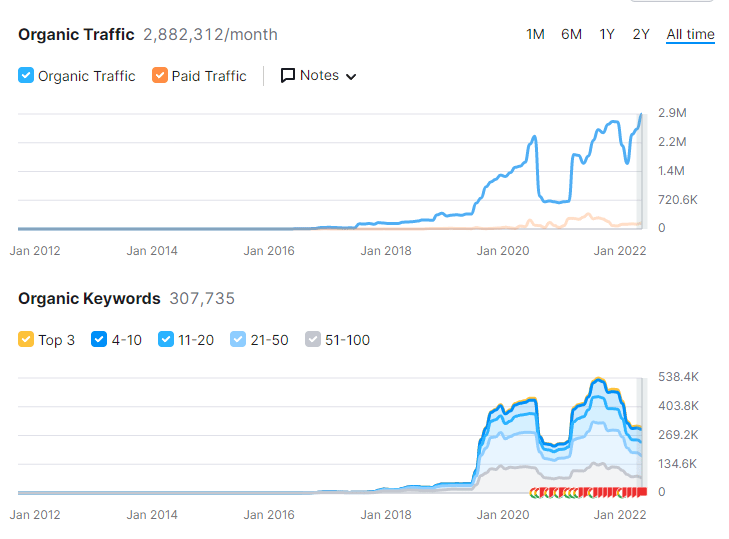
The Google Search Console Graphic for organic search performance of entity-oriented search SEO project for the last 3 months is below.
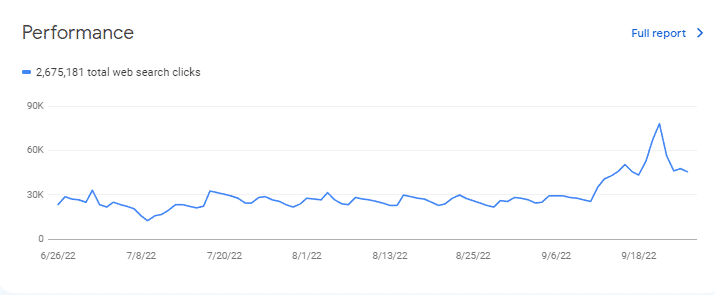
The extended look of the Google Search Console Performance report for the Entity-oriented Search case study is below.
To understand Google’s possible perspectives for reversing effects between May 2022 and September 2022 Broad Core Algorithm Updates while diversifying the results further, read the Topical Consolidation and Broad Index Refresh concepts.
What is Topical Consolidation for Search Engines?
Topical consolidation is the process of involving only certain topics by increasing the contextual relevance between the different website segments. Topical consolidation helps websites to improve their topical relevance for a specific topic by deepening their expertise for a single vertical. Topical consolidation might be done via website owners or search engines from different points of view. A search engine might rank a website higher for a certain topic while removing it from the SERP for another topic. A web source might be a topical authority for a topic while an amateur for another. And, non-quality and non-accurate information from a section might affect the rankailibty of another section. Thus, a website that focuses on only connected topics, and contexts has a better topical consolidation. And, a search engine might combine local relevance, audience relevance, language closeness of the audience to the topical relevance. Sometimes Google might translate a document to another language automatically, and rank it as stated by Google.
Topics consist of contexts and concepts. Every concept is an entity, even if it doesn’t have a name. And, every entity is also a topic that aggregates different query networks even if there is no single context. And, every context is unified with a concept and topic. For example, “Christiano Ronaldo” is not a concept, but he is a footballer, and “footballer” is a concept that signals an occupation, professional career, talent, and sports personality. Christiano Ronaldo is a topic that might have certain types of contexts such as “best footballers”, or “extraordinary personality footballers”. One focuses on skill, one focuses on personality which is different contexts around the same personality type of entity. According to the web source’s focus, the topical consolidation might happen. For a psychology website, the personality might be more important, while for a sports web source the skill might be more important. As it is stated in the Helpful Content Update, stay in the context while defining the concept.
What is Broad Index Refresh?
Broad Index Refresh is a process to refresh the ranked or retrieved documents for certain queries. Index refresh is happening continuously for Google since the Google Caffeine. But, Broad Index Refresh means that the search engine needs to remove certain resources from certain topics and query networks and add new ones. A search engine might not use all the resources all the time. Finding new resources, processing their content whether text or visual, and comparing it to the others, ranking the source, testing the source, and collecting the data is costly.
Every day there are 252,000 new websites are created. Thus, search engines might start to test the new websites with regular frequencies with a candidate web source filtering system. The filtered web source candidates for certain topics might be started to be ranked and tested for further rankings. Broad Index Refresh helps for topical consolidation by removing the lesser quality resources. To understand the “quality thresholds” with “comparative ranking”, and why some websites are losing the broad core algorithm updates even if they have good content, understand the Index Refresh. Inverted Indexes are regularly refreshed, and a search engine might see the causation between more diversified-authoritative web sources and user satisfaction.
How do Different Broad Core Algorithm Updates focus on Different Tasks?
Different Broad Core Algorithm Updates might focus on different tasks. One of the Broad Core Algorithm Updates might focus on topical consolidation for web sources to provide index refreshment to include more sources with new distributed ranking prioritization for certain topics while another one focuses on choosing the new web sources to rank for certain topics. Sources that publish an extensive amount of content for a single, or connected multiple topics might gain new queries to gain first impressions and historical data to be evaluated as a candidate after a certain amount of historical data. But, some sources might not exceed the quality thresholds due to lack of coverage, or information quality and responsiveness. Sources that do not publish consistently, or comprehensively might be eliminated. On the other hand, some sources might continue to increase their rankings while the search engine gives them more queries from a context even if they make them lose traffic from others.
Why did May 2022 BCAU Affect the website Negatively?
The May 2022 BCAU affected the website negatively because the source has been evaluated by the search engine for topical consolidation. For the November 2021 Broad Core Algorithm Update, the source increased its organic traffic while losing organic queries that are not relevant enough. The lost organic queries might affect the relevance of a web source to a specific topic. Semantic relevance between the queries and their overall consolidation helps a web source to propagate its topical consolidation. To rank for a specific phrase taxonomy such as “digital camera for underwater”, the “digital camera”, and “camera” matter separately. A source that loses its connection to the concept of “camera” would lose its overall rankability for “digital camera”, or “digital underwater camera” as well.
Search engines calculate and adjust the relevance of queries, and relevance from a query to a topic, and from a topic to a source while from a document to a query during the update. A broad core algorithm update does all these at the same time while refreshing the entire index. Thus, with the contribution of machine learning, the Ranking State (direction) might cause ranking functions and reverse the traffic. The Organic Traffic loss from the May 2022 Broad Core Algorithm Update was especially from the educational materials, and in the next section, you can see how further contextual consolidation helped for further rankings.
What did Entity-oriented Search Project Change?
Entity-oriented search SEO Case Study and Project started to change the sections below after the decision of the May 2022 Broad Core Algorithm Update.
- Focusing on more educational topics, and contexts.
- Covering educational books, lectures, research, and researchers.
- Focusing on university materials, professor, and their work.
- Focusing on exams from different educational layers and levels along with their books.
- Connecting the educational need materials to the stationary e-commerce pages.
- Extending the contextual coverage to the scientific research and study topics.
- Extending the contextual coverage to the school lectures, their topics, and necessary books.
- Focusing on the school ages, and school-related children’s books.
- Extending the coverage to the student needs, and student lifestyle.
- Increasing the coverage for the internal links, and anchor text for a better-directed graph over all of these context domains.
Why did September 2022 BCAU Affect the website Positively?
The source increased its featured snippet and PAA gaining, and it started to rank higher for all the university exams, university, and every grade-of-school degree. All the educational topics are connected back to science, and literature, along with person-type of entities. The higher amount of connection with more contextual consolidation helped the web source to overcome the competitors by regaining the positive ranking state.
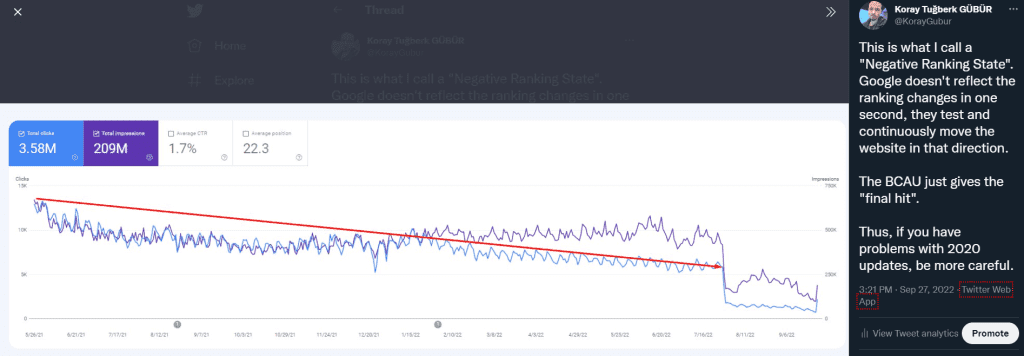
This is the fourth update of the Importance of Entity-oriented Search SEO Case Study, and as Holistic SEO, to focus on new SEO Case Studies, and since this case study made its point as evergreen against the time that passed, and will pass, this might be the last update.
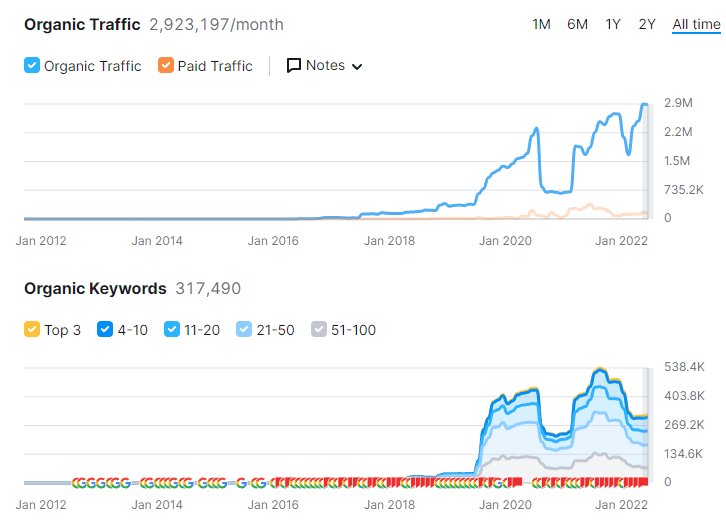
Last Thoughts on the Importance of Entity-oriented Search Understanding for SEO
Entity-oriented search understanding is not popular as AI Text Generation. But, whether it is Natural Language Understanding or generating text, the entities, and entity-oriented search is the center and heart of these processes.
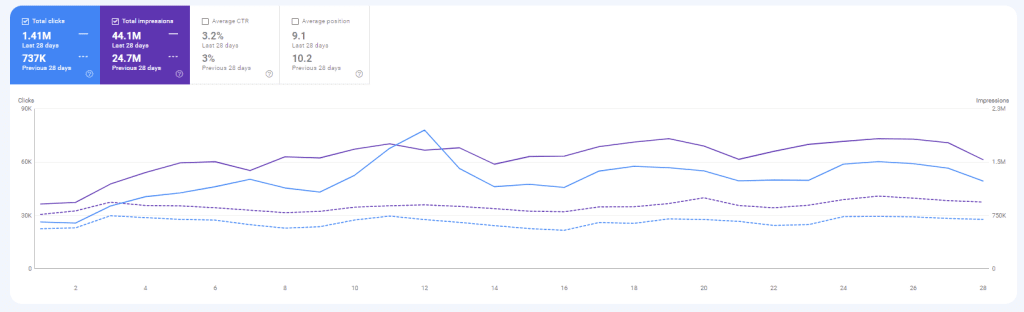
The person who understands the entities, their nature, their possible connections, search engines’ perspectives for these entities, possible functions, actions, and definitions for these entities will create the difference between conventional SEO and Holistic SEO. To implement the entity-oriented search principles, an SEO should perform experiments with the entities, and their attributes by creating hyper-structured data. To make the information extraction easier, different sentence structures for different questions can be used to implement entity-oriented SEO A/B tests.





Great coverage. Love to show you what we did using Innlink, SEM rush and our own product Schema Manager. Let’s connect. I will ask Dixon to introduce us.
Thank you, Benu! Happy to hear your kind words.
Great article Koray! I love the idea of using the pages the client already had in place and just bridged them together with all the pages by “book genres”, “books from different countries”, etc. Seems like a very effective way to improve topical authority and make connections between all those entities.
Thank you, Jeff! I am glad that you liked it!
Thank you so much, Koray. You’re adding super great value to the SEO field. I much enjoyed your attention to details. I think your technique is very close to the Wikipedia structure. I’m planning to apply your strategy on my website, but I have one question for you, is there any definitive steps/guide on creating a topical map? Thanks a million
Inlinks has built out this methodology.
Semantic yaklaşıma olan ilgim seni takip ettiğimden beri çok arttı. Çok teşekkürler.
Hoşgeldiniz 🙂
[/Thank you]
Excellent work – One of my favorite articles about the importance of topical authority
That’s kind of you to say. Koray’s good, isn’t he?
Amazing article, thanks!
“All these 5 entities are from the same type which is country, thus they will have the same main attributes. The attribute hierarchy or semantic dependency tree of the attribute can be used to understand the priority of the attribute to define an entity. If a search engine sees these 5 attributes on a web page”
In the above paragraph, I think the word “attribute” should be replaced with “entity”, in one or more instances.
Thanks. I think that is better, now.
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!