Imagine having two chefs in a kitchen, vying to prepare the same dish. While they might both be talented, their efforts could clash, leading to confusion and potentially subpar results.
The same analogy applies to websites with overlapping content.
When multiple pages target the same keywords or topics with similar search intent, they compete, leaving search engines unsure which page to prioritize for a specific search query. This phenomenon, known as content cannibalization, sabotages your website’s potential.
This article will explore the issue of content cannibalization, its underlying causes, and effective solutions.
What is Content Cannibalization?
Content cannibalization is when multiple pages on your website compete for the same or similar keywords and search intent. This can happen in several ways:
- Targeting the same keyword: You have multiple pages targeting the same keyword or phrase, confusing search engines about which page to rank higher.
- Covering similar topics: You have several pages covering similar topics, diluting the overall authority of each page and making it harder to rank them well.
- Overlapping content: Your pages have very similar content, offering little unique value to users or search engines.
What Causes Content Cannibalization?
Keyword cannibalization can arise from various factors. Let’s dive into some common culprits:
Topic cannibalization
When more than one page covers a specific topic, search engines often struggle to determine which page should take precedence for specific queries. This confusion undermines the authority of each page, as search engines may hesitate to prioritize any single page over the others, resulting in diminished rankings for all competing pages.
Topic cannibalization can arise from various factors, including improper internal linking, content syndication, boilerplate content, or unintentional replication due to content management system (CMS) issues.
When you bring your content pages into InLinks, the tool can show you those topics that may be cannibalized by multiple pages. Associating each page to one topic on InLinks can help tackle the cannibalization, as it shows Google and other search engines the most important pages about specific topics on your website.
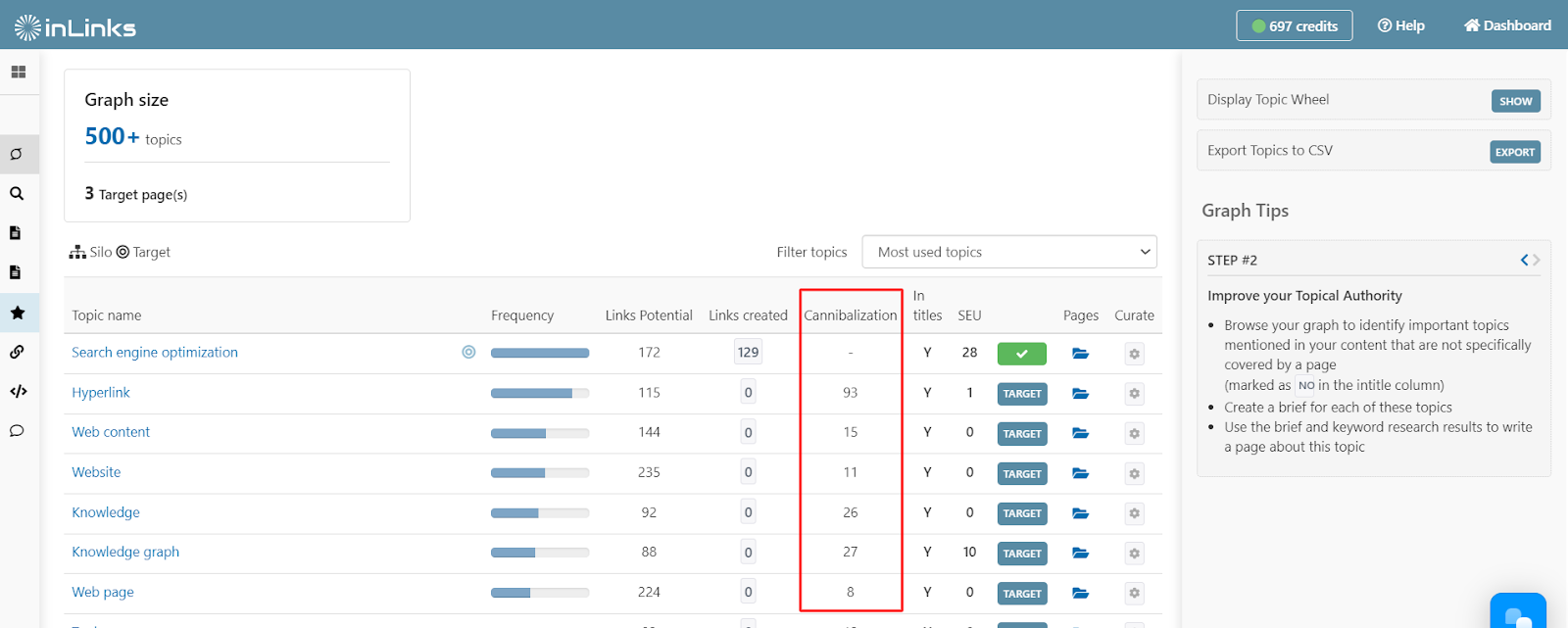
In addition to that, adding InLinks web page schema to your content provides more clarity to Google as to the most important pages for each topic on your site.
Exact Match Linking
Exact match internal linking involves using the precise keyword you want to rank for as the anchor text within your internal links. For example, if your target keyword is “vegan baking recipes,” your internal links from other pages on your site would also use the exact phrase “vegan baking recipes.”
However, when you use the exact same keyword repeatedly in internal links pointing to multiple pages, search engines struggle to understand which page is the most authoritative and relevant for that keyword. This uncertainty leads to your pages competing against each other for ranking positions, causing cannibalization. Instead of one strong page ranking well, you might have several pages ranking moderately or poorly.
Moreso, search engines like Google have historically deemed excess exact match internal linking as manipulative and unnatural. Specifically, Google’s Penguin update targeted websites with unnatural link profiles, including overuse of exact match anchor text.
Lack of Canonicalization
The canonical tag, typically added to the HTTP header of the cannibal page, serves as a pointer to the preferred page. Here’s an example of how it looks:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.website.com/preferred-page/” />
Without proper canonicalization, search engines may receive conflicting signals regarding which version of the content to prioritize in search results.
Consequently, keyword cannibalization may occur when search engines opt to rank a different version of the content than intended by the website owner, resulting in suboptimal rankings and traffic distribution.
Flawed Keyword Research
Many adopt the standard keyword research method, which entails compiling a list of similar keywords and creating different content pages for every slight variation based on monthly search volume. For example, creating different pages targeting “Home insurance” and “House insurance.” However, this approach is flawed because multiple search phrases can have the same intent and map to the same topic, so creating different pages for each keyword variation is redundant and causes cannibalization.

InLinks’ recommended new approach to keyword research
Dangers of Content Cannibalization
Content cannibalization hurts websites in many ways, including:
Dwindling Page Authority
Think of competing pages as contestants in a popularity contest. When multiple pages vie for the same keyword, they spread their “votes” thin—links, mentions, and search signals become divided. Consequently, search engines struggle to ascertain which page merits the top spot, resulting in diminished rankings for all contenders. This dispersion of authority around the topic weakens the credibility, quality, and relevance of each individual page.
Depletion of Google’s Crawl Budget
Search engines operate within constraints, with limited resources for crawling and indexing websites. In instances of content cannibalization, where conflicting signals confuse search engines, Google might squander its crawl budget, attempting to decipher which page holds greater relevance. Consequently, precious resources are diverted away from crawling and indexing other crucial pages on your website, impeding their visibility and potential for ranking.
Reduces Conversion Rate
Imagine someone searching for “best running shoes” and landing on a page about hiking boots. They’ll likely click away in frustration. This is the reality of cannibalization. Users land on the wrong page, get confused, and leave, leading to a higher bounce rate and low conversion rate.
How to Identify Content Cannibalization
Identifying keyword cannibalization requires a combination of technical tools and manual analysis. Here’s how to approach it:
Search Your Website
Begin by searching on Google with this search operator:
site:[yourdomain.com] [target keyword]
This operator shows all indexed pages for a specific keyword. If you see many similar pages, it might mean there’s cannibalization.
For instance, below is what comes up when I look up site:inlinks.com seo
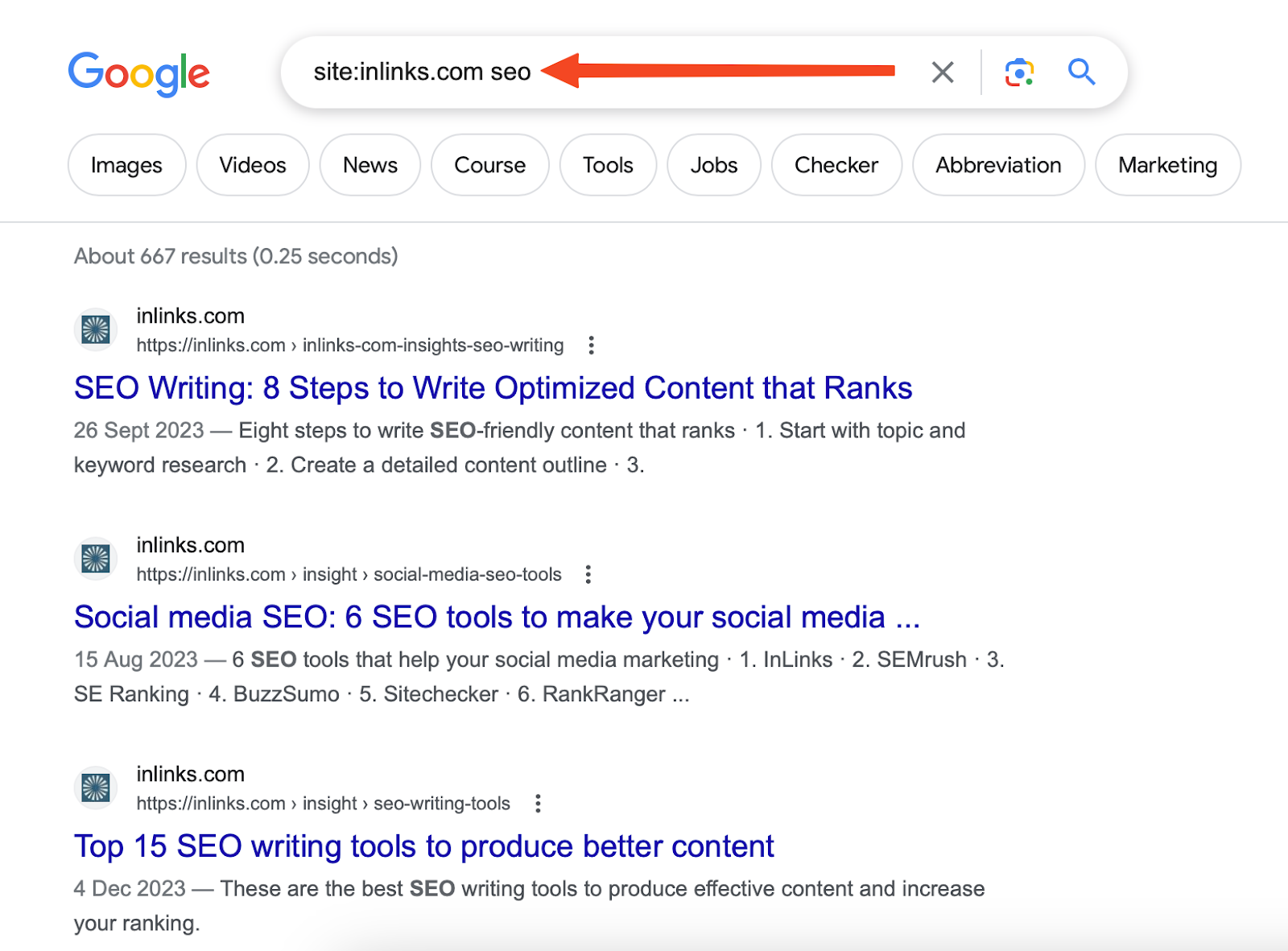
InLinks’ indexed pages for the ‘SEO’ keyword
Although InLinks has multiple pages ranking for ‘SEO,’ they are quite distinct from each other and cater to different search intents, showing no sign of cannibalization.
Dive into Google Search Console
Explore the “Search results” section of Google Search Console to analyze ranking keywords and their corresponding URLs. Identify cases where multiple URLs compete for the same keyword and assess whether they serve distinct user intents or offer significantly different content. If you find multiple URLs with similar content and targeting the same user intent, it could indicate potential content cannibalization.
Track Keyword Rankings
Monitor the rankings of multiple pages targeting identical keywords. Simultaneous drops in rankings across these pages could be a strong indication of cannibalization, necessitating further investigation and corrective measures.
Analyze Traffic Patterns
Also, examine traffic patterns and user behavior using Google Analytics to identify pages suffering from misplaced visibility due to cannibalization. Pages covering similar topics but receiving significantly less traffic may indicate confusion for the search engine and users. Analyzing traffic patterns helps pinpoint areas where optimization is needed to improve user navigation and engagement.
6 Ways to Fix Content Cannibalization Issues
Once you identify cannibalizing issues on your website, implementing these strategies can help you tackle them and give your SEO a boost:
1. Embrace Keyword Clustering
Instead of creating a whole article for every keyword variation you find during keyword research, use keyword clustering to target similar keywords with one article. Keyword clustering groups similar intent search terms and their synonyms to create authoritative pieces that target topics as a whole rather than individual keywords. This approach ensures each page offers thorough content that could rank for multiple related keywords, reducing the risk of cannibalization.
InLinks is a valuable tool for automating topic clustering. It leverages semantic analysis and Natural Language Processing to understand the meaning behind topics and then groups the search terms searchers use to find those topics into meaningful keyword clusters. Here is a helpful post on how to conduct keyword clustering with InLinks.
2. Consolidate Duplicate Content
If you have multiple pages with very similar content, merge them into a single, comprehensive page that covers the topic in depth.
Let’s say you run a blog focused on sustainable living. You have several blog posts on various aspects of eco-friendly home cleaning, such as:
- “5 Natural Cleaning Products You Can Make at Home”
- “DIY Cleaning Solutions for Every Surface”
- “Green Cleaning on a Budget: Tips & Tricks”
While each post offers valuable information, they tackle the same core topic: eco-friendly cleaning. Consider merging them into a comprehensive “masterpiece” post. This resolves cannibalization and enriches user experience while boosting SEO performance.
3. Diversify Internal Linking Anchor Texts
Your anchor text hints Google about the content of each page on your website. If you link different pages with the same anchor text, you send mixed signals to the search engine as to which page to prioritize for the keyword in your anchor text — essentially diminishing the authority of each page and dividing link equity.
A better approach would be to diversify your internal link anchors using synonyms, related keyword phrases, and sentence fragments that are clear and descriptive to:
- reflect the content of each linked page
- improve the user and search engines’ understanding of your pages
- and promote natural link-building.
4. Redirect Low-Performing Pages
Identifying and redirecting low-performing pages to the most relevant existing page with a 301 status code can help tackle cannibalization and boost your SEO. For example, if you have two articles on your travel blog covering a similar topic, you could redirect traffic from the low-performing article to the high-performing one to help consolidate authority and enhance ranking while eliminating cannibalization.
5. Leverage Canonical Tags
If your website has multiple pages with similar content, use canonical tags to designate the ‘master’ page that search engines should prioritize in indexing and ranking. This practice mitigates duplicate content issues, ensuring that your preferred page receives optimal visibility and ranks well for target keywords.
6. Monitor and Track Results
Regularly monitor keyword rankings, organic traffic, and user engagement metrics to assess performance after implementing content cannibalization fixes. Tools like Google Search Console and Google Analytics can be valuable for tracking these metrics.
How NOT to Fix Content Cannibalization
Content cannibalization can frustrate your SEO efforts, but resorting to quick fixes can do more harm than good. Here’s what you should avoid when tackling this issue:
1. Bulk Noindexing
While noindexing can be useful for specific pages (e.g., filter pages), indiscriminately using it on pages with valuable content or potential traffic is a mistake. This prevents search engines from crawling and indexing them, leading to a loss of visibility and potential ranking opportunities.
2. Keyword Stuffing
Manipulating keyword density by stuffing them unnaturally into your content can trigger Google penalties and harm your ranking. This tactic offers no value to users and is easily detected by search engines.
3. Deleting Content
Simply deleting content, even seemingly duplicate pages, can sometimes have negative consequences like broken internal links, lost backlinks, and potential drops in organic traffic. It can also signal to search engines that your website is unstable or unreliable. Before deleting duplicate content, consider consolidating them and redirecting any existing links to the new improved content.
4. Creating Doorway Pages
Deceptive tactics like doorway pages, designed to redirect users to another page after landing, are strictly against Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. These pages can result in manual penalties, harming your website’s ranking and overall reputation.
Stop Cannibalization and Build Lasting SEO Success
Sustainable SEO success lies in creating high-quality content that provides value to your audience and the search engine. However, cannibalization can dilute your SEO efforts and make it difficult to achieve success. Instead of creating multiple pages of weak content that water down the value of your website, focus on producing a few unique and meaningful pages that are useful to users. Also, avoid quick fixes that prioritize search engine manipulation over genuine user experience and content quality. By implementing ethical and strategic approaches, you can effectively address content cannibalization and achieve long-term SEO success.
| This post was researched and drafted by Juliet John and reviewed and edited by Dixon Jones. |




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!